Heatwave In India: Tips And Preventive Measures To Manage Heat Oedema
Heat oedema is a condition that happens due to the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues due to high temperatures. While the condition doesn’t cause any major health issues, it can be uncomfortable and aggravate certain health conditions. Read on to know some of the tips and preventive measures to manage heat oedema.
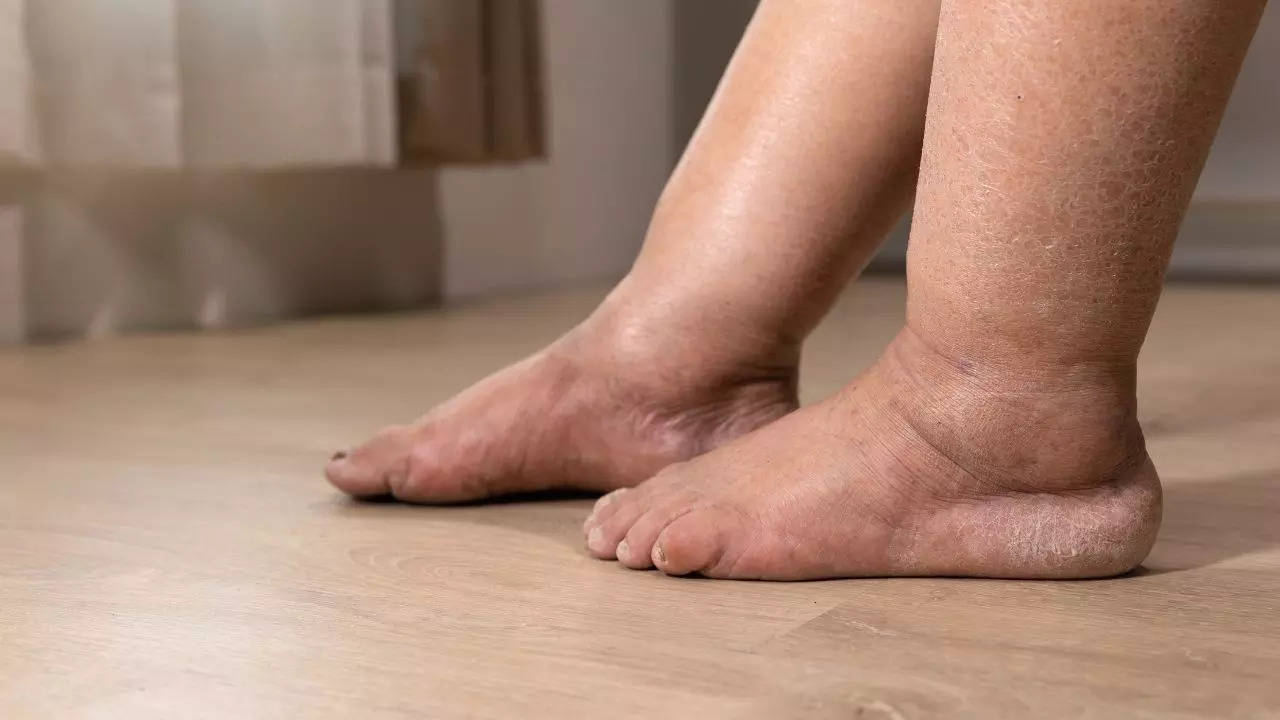
Check Here The Tips And Preventive Measures To Manage Heat Oedema
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has said that heatwave to severe heatwave conditions are expected to persist in several regions of the country. Several states have recorded temperatures as high as 43 to 46 degrees. The government has issued a health warning. It is also important that people take necessary precautions to keep themselves protected from heat-related illnesses. Heat oedema is a condition that is caused due to high temperature which leads to swelling in the hands and legs.
Heat oedema is a condition that happens due to the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues due to high temperatures. This usually happens during hot weather conditions or in places where there is excessive heat. Heat oedema usually affects the lower parts of the body such as the feet, ankles, and legs.
Prolonged exposure to heat leads to vasodilation which causes blood vessels to expand and allows fluid to leak to the surrounding tissues which eventually causes swelling. While the condition doesn’t cause any major health issues, it can be uncomfortable and aggravate certain health conditions such as cardiac issues. Therefore, if you’re suffering from heat oedema, it is important that you take the necessary precautions to keep yourself protected and manage the condition. Here, take a look at some of them.
Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is important in preventing heat oedema. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially when you’re exposed to high temperatures or perform any physical activity. Choose water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables as they can supplement your fluid intake.
Avoid Exposure To Heat
Reduce the time you spend in hot environments, especially during peak sun hours. Stay under the shade, use umbrellas or hats and wear lightweight, breathable clothing to reduce heat absorption and reduce the risk of swelling.
Keep Your Feet Elevated
When you’re resting or sleeping, try and keep your feet at an elevated place. This helps to improve blood circulation and reduce fluid retention in the lower parts of your body. Stack your pillow one above the other and keep your feet above it to reduce the swelling.
Cool Compresses
Apply cold compresses or ice packs to swollen areas to constrict the blood vessels and reduce inflammation. Wrap the compress in a towel to prevent direct contact with your skin and limit application to 10-15 minutes at a time to avoid any damage to the skin.
Sodium Intake
Excessive consumption of sodium can lead to fluid retention and aggravate the swelling. Limit the intake of processed foods, fast food and other snacks that have high amounts of salt in them. Instead, opt for fresh, whole foods rich in potassium, which can help maintain fluid balance in the body.
Exercise
Practice low-impact exercises like walking or swimming as these can improve circulation and prevent the buildup of fluid in the body. Also, try and avoid any strenuous activities in extreme heat because excessive sweating can lead to dehydration and eventually cause swelling.
Avoid Hot Showers
Hot showers can aggravate heat oedema by increasing your body temperature and increasing vasodilation, leading to higher fluid retention and swelling. To prevent this, opt for lukewarm or cool showers as it can help regulate your body’s temperature and reduce the risk of heat-induced swelling.
Staying In Air Conditioned Spaces
Using air conditioners can help you in managing the conditions. Air conditioners help to regulate indoor temperatures, thereby, making the environment cooler and more comfortable. This eventually helps to reduce the risk of heat-related swelling.
Trending:
End of Article
Subscribe to our daily Lifestyle Newsletter!
Related News





5 Signs You Have Sprained Your Foot Or Ankle

Continuous Eye Rubbing Leads Malaysian Man To Cornea Transplant Surgery

Fatigue To Blurred Vision: 5 Warning Signs Of Prediabetes You Should Not Ignore

Smoking Rises By Two-fold Among Teen Girls In India, Says Report; Know The Drastic Health Risks

5 Supplements That Secretly Do More Harm Than Good To Your Health









